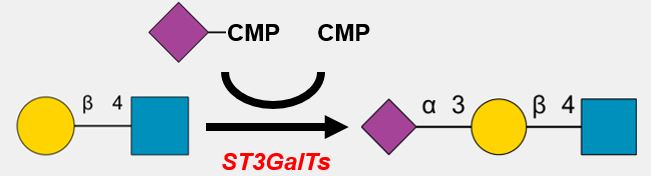
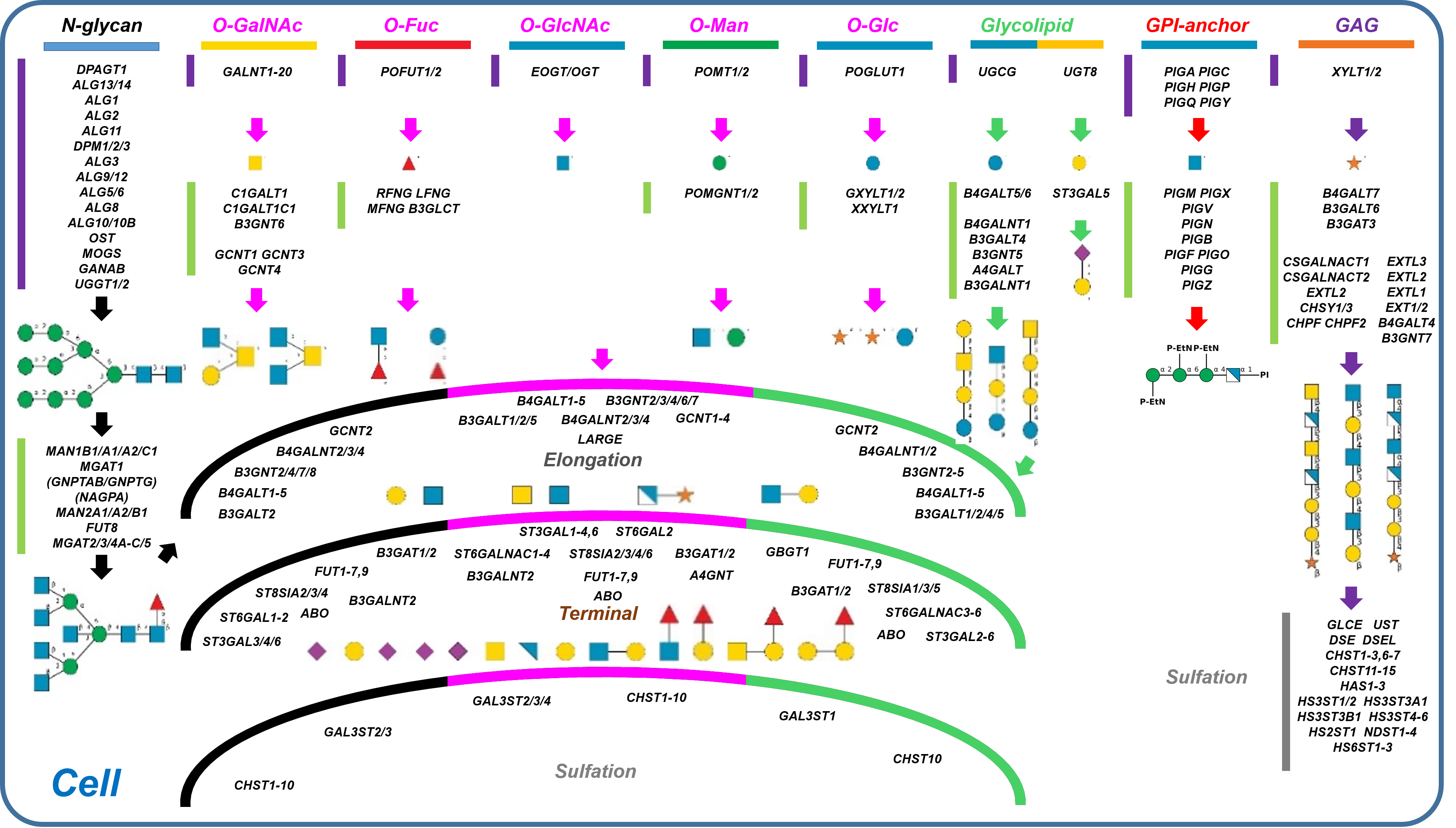
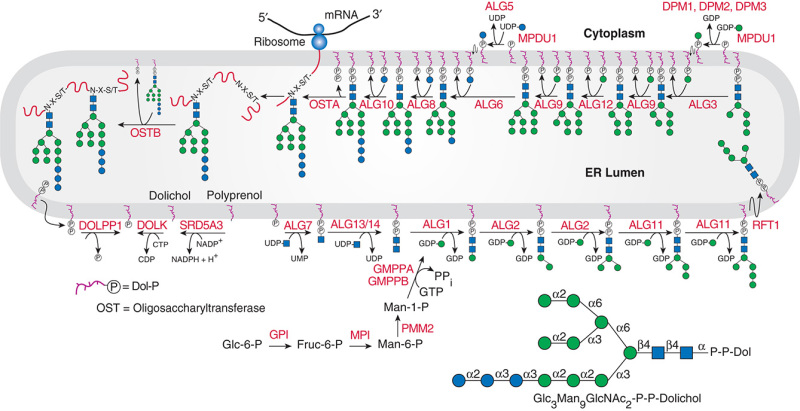
GlycoEnzDB
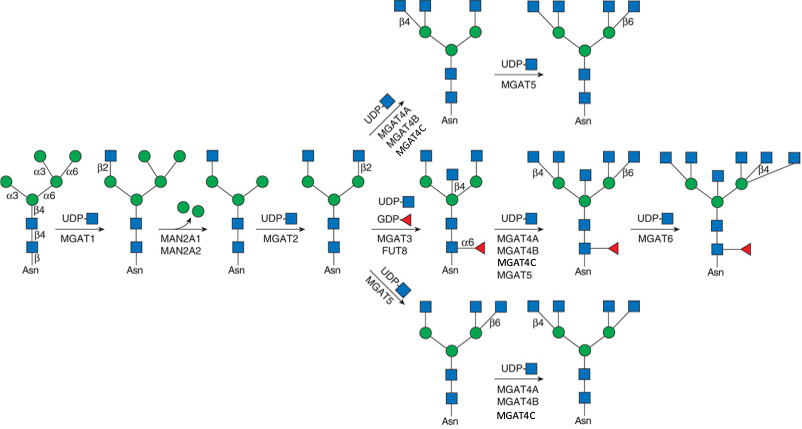
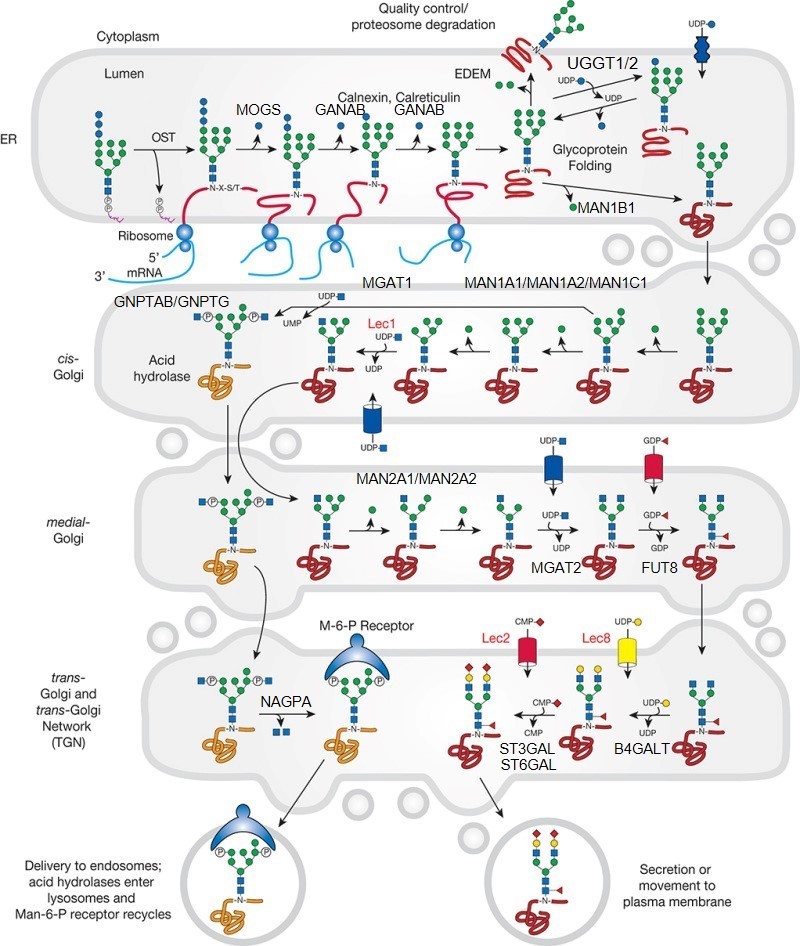
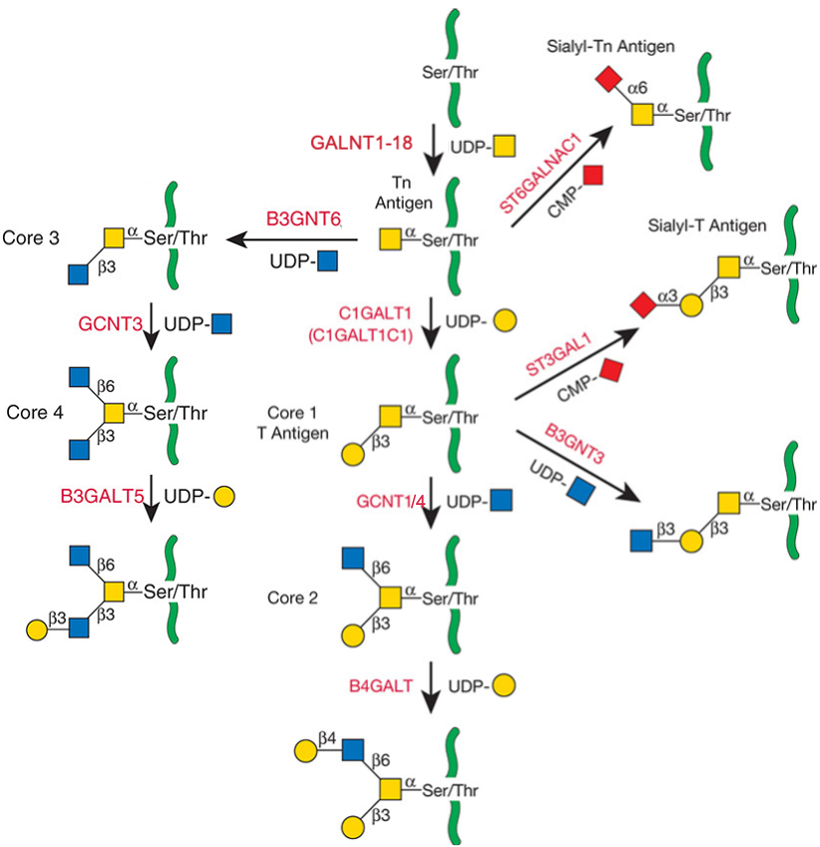
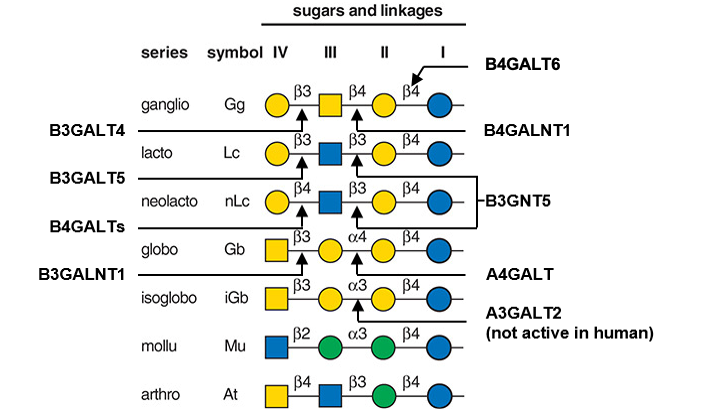
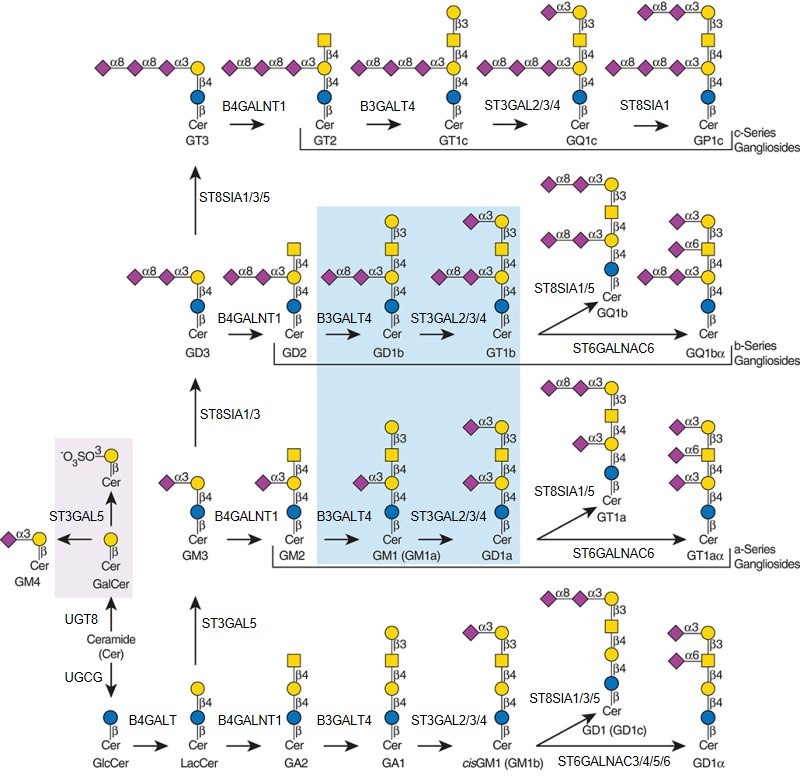
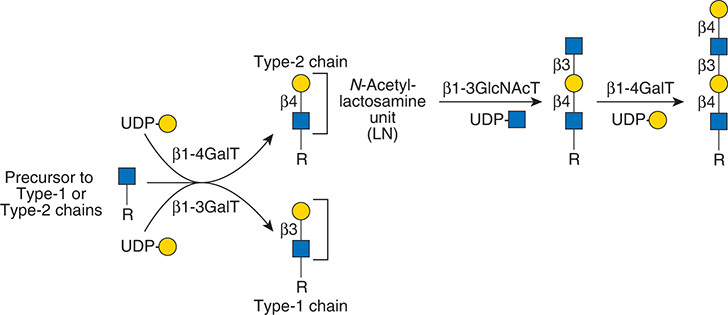
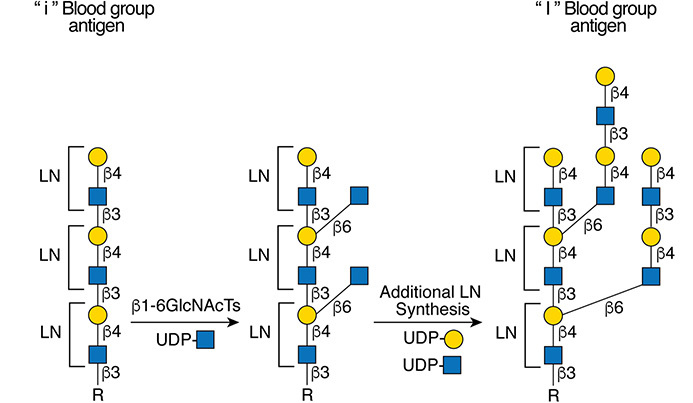
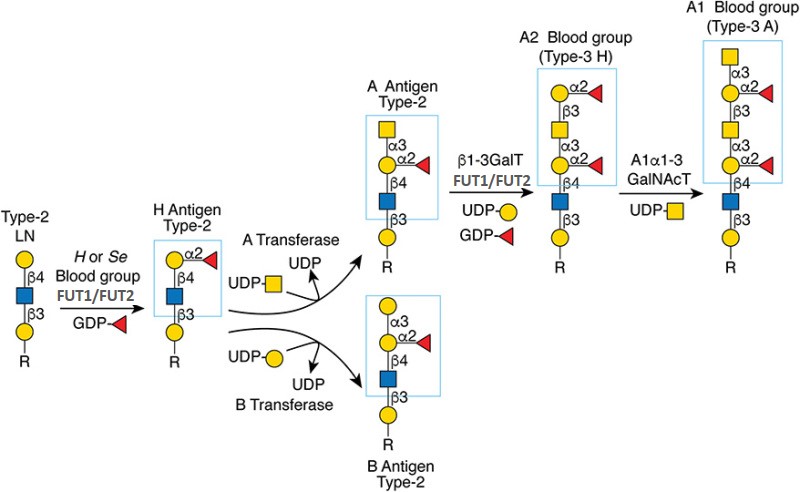
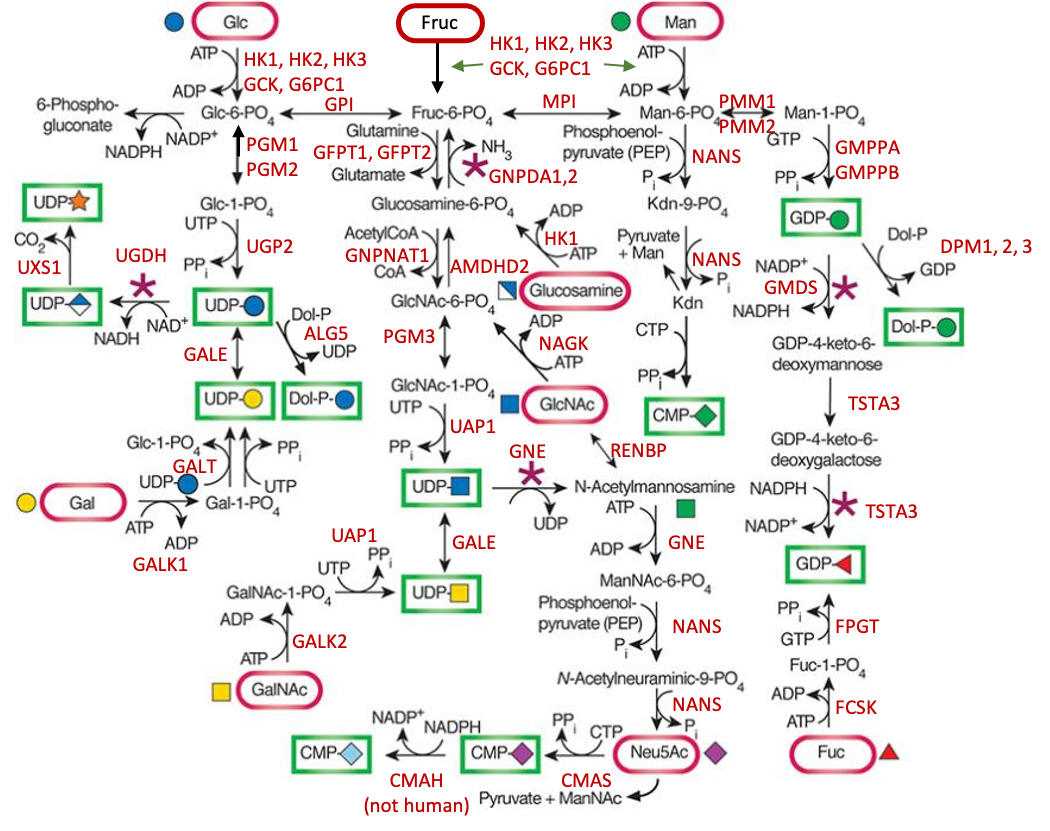
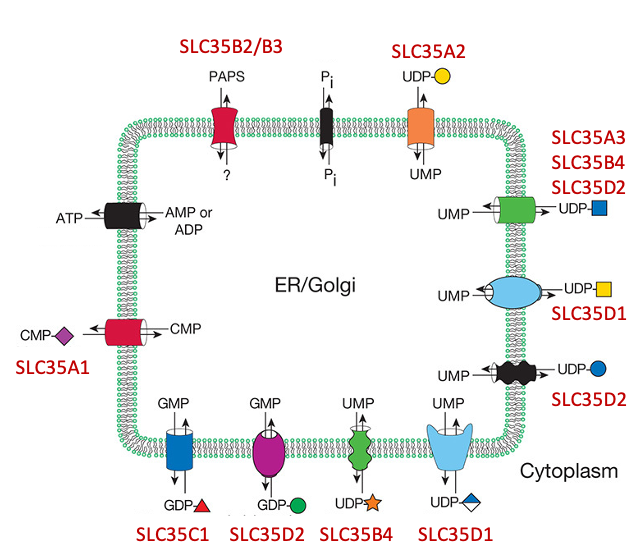
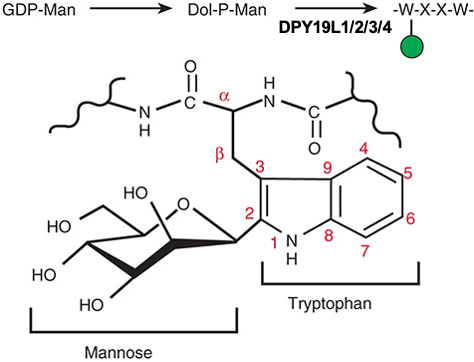
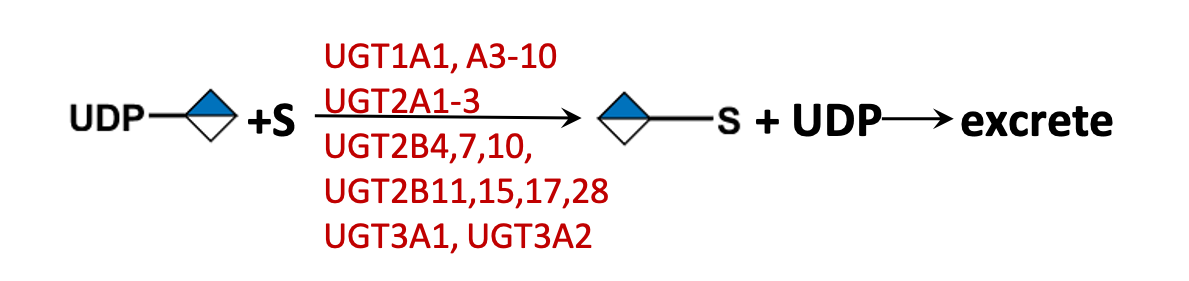
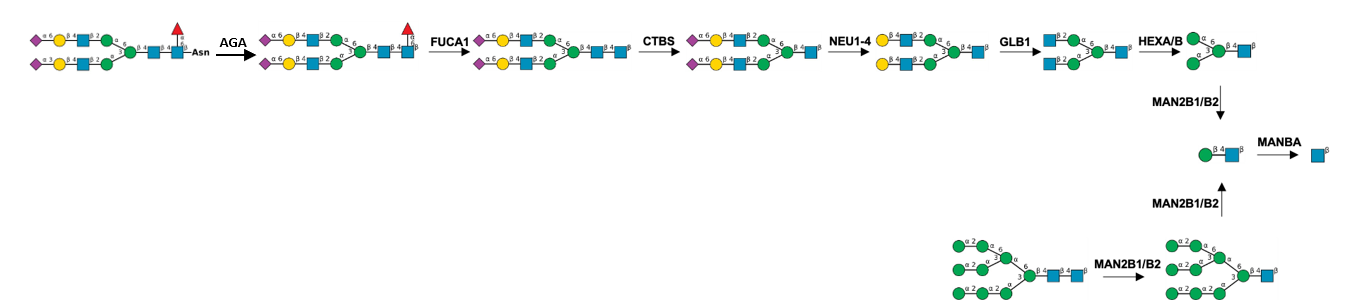
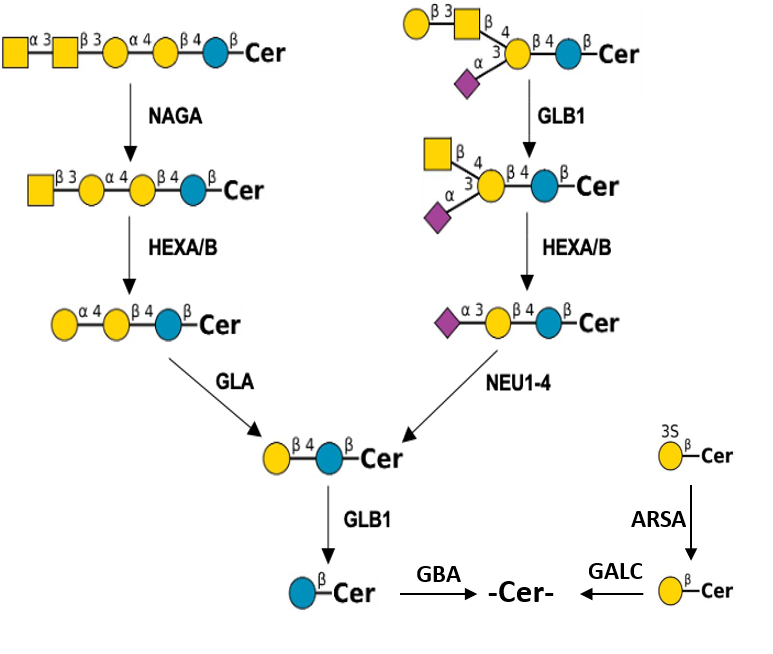
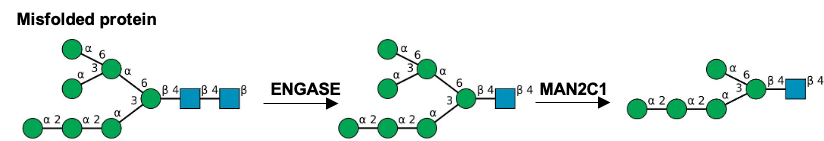
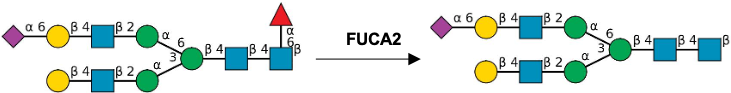
Description: The GlycoEnzDB is a manually curated glycoEnzyme database, primarily focused on humans. It covers 390 enzymes across 28 pathway maps. Facilities are also available to create custom glycosylation reaction pathways using experimental data in SBML format and for pathway simulation
Contacts: Sriram Neelamegham (neel@buffalo.edu), Yusen Zhou (yusenzho@buffalo.edu) or Ted Groth (tgroth@buffalo.edu).
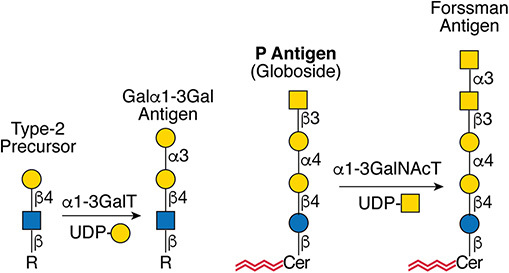
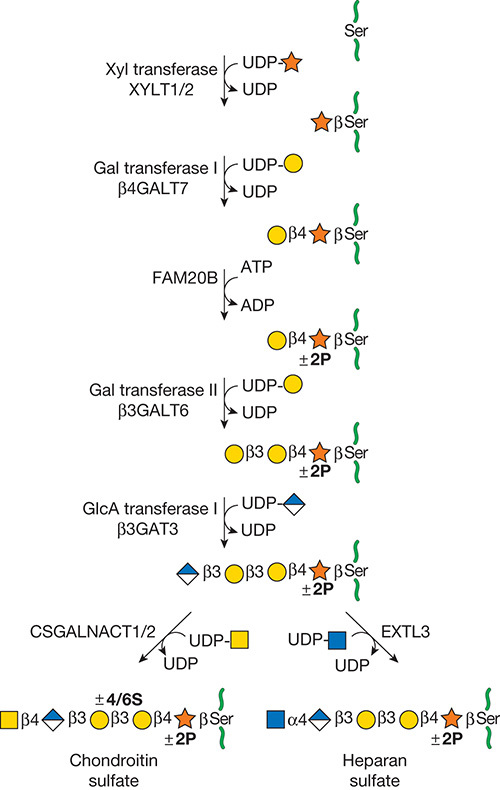
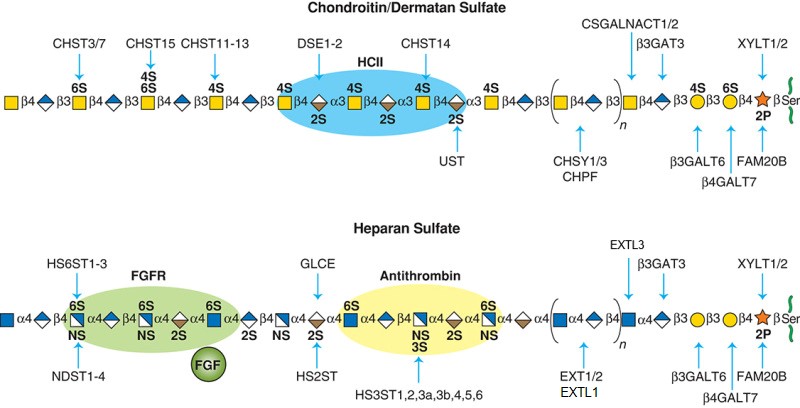
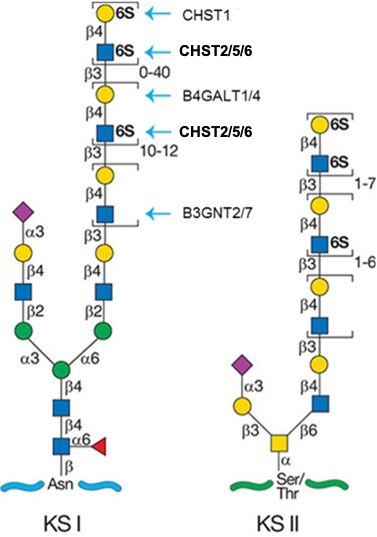

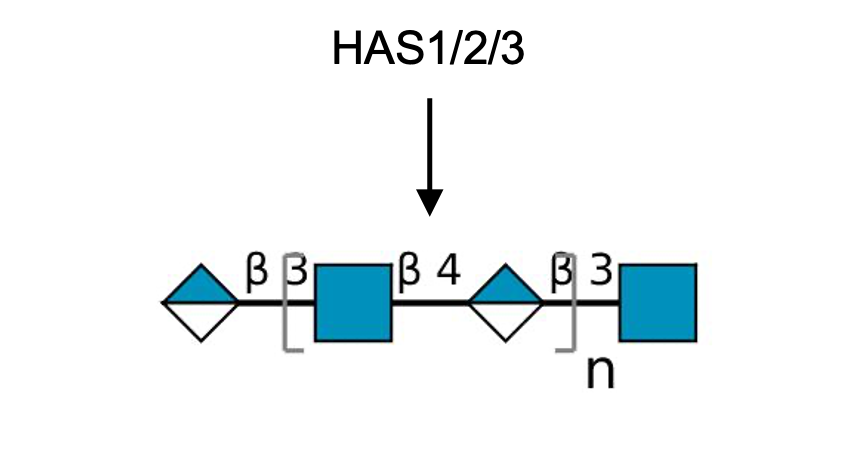
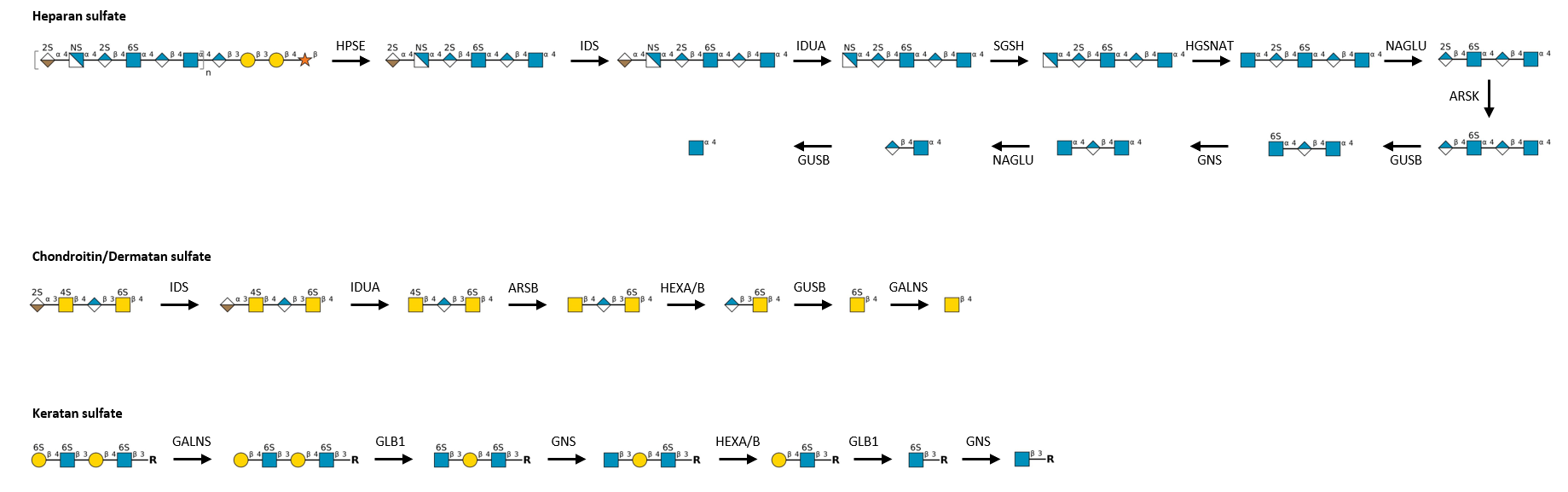
.jpg)
GlcA(b1-3).jpg)
GlcNAc(a1-4)GlcA(b1-3).jpg)